NHN Provider Resource Library
MEDICAL RISK ADJUSTMENT
Nebraska Health Network offers a number of educational resources to help advance our mission of delivering patient-centered, high-value care.
Medical Risk Adjustment and Coding Best Practices Resources
EDUCATION MODULE
Medical Risk Adjustment Education Module
MRA helps health insurance payers – including Medicare – understand how sick your patients really are, as indicated by their risk scores. MRA is used in value-based models to ensure that cost targets are adjusted to align with the illness burden of the population. The NHN has created a quick 15-minute video to help you understand how MRA works, and what you can do to insure you are not penalized for taking care of sicker patients.
Medical Risk Adjustment v28 Quick Reference Guide
Download this high-level overview of Medical Risk Adjustment. This document is not intended to be a comprehensive list of all Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCCs)/International Classification of Disease codes (ICD-10s). Following each HCC is the corresponding Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) for the condition. Please note that the best practice is to also document and code for related complication(s).
PROVIDER RESOURCES
Medical Risk Adjustment Overview
This educational resource guides providers on the importance of Medical Risk Adjustment, specific to Medicare. It helps educate providers and coders on what MRA is, why it is important, how to optimize risk capture and a quick example of how it works including an overview of M-E-A-T documentation.
Coding Social Determinants of Health in Patients: Z code Pocket Guide
Z codes are an efficient way to capture Social Determinants of Health impacting patients. The use of Z codes helps:
- Communicate patient barriers to others on the care team
- Helps providers consider barriers when making treatment decisions
- Helps document social risk factors to depict the overall patient health status
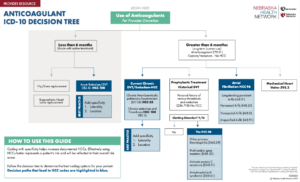
Anticoagulant: ICD 10 Decision Tree
Coding with specificity helps increase documented HCCs. Effectively using HCCs better represents a patient’s risk and will be reflected in their overall risk score. Follow this decision tree to determine the best coding options for your patient. Decision paths that lead to HCC codes are highlighted in blue.
Managing Obesity in Patients
According to the CDC, more than 40% of U.S. adults are obese. Obesity is a complex condition that can lead to serious health issues including diabetes, heart disease and cancer. NHN's provider resource includes tips for talking with patients, accurately coding for obesity and more.
Behavioral Health in Older Adults: Screening and Coding Guidelines
Although common in older adults, depression is not a normal part of aging. Depression is a serious mood disorder that may cause severe symptoms that impact how a person feels, thinks and handles daily activities. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, one in six seniors suffer from depression. Prevalence is highest for beneficiaries with comorbidities like cancer, arthritis, stroke, chronic lung disease and cardiovascular disease.
Download our Behavioral Health in Older Adults: Screening and Coding guidelines to review what to look for, how to screen patients and how to code.